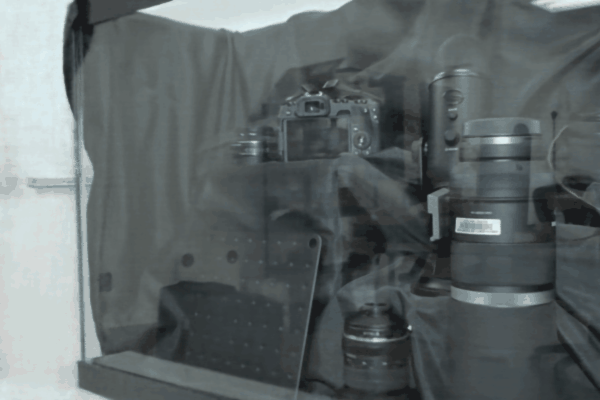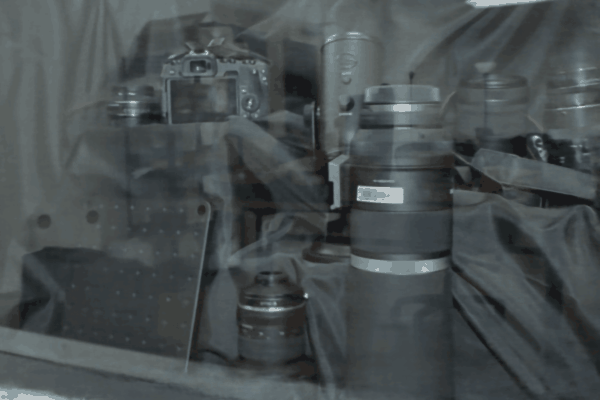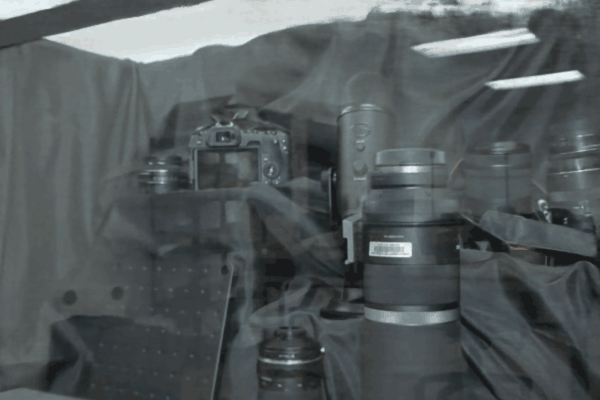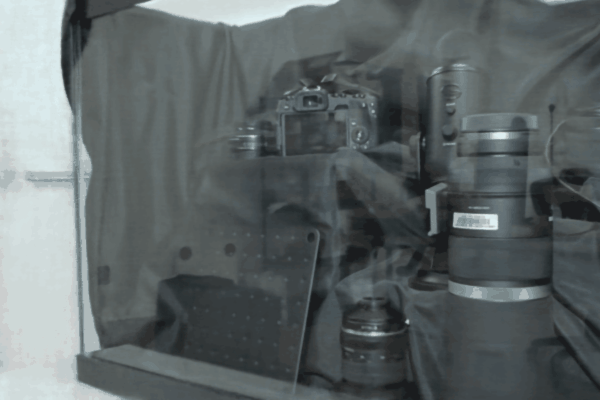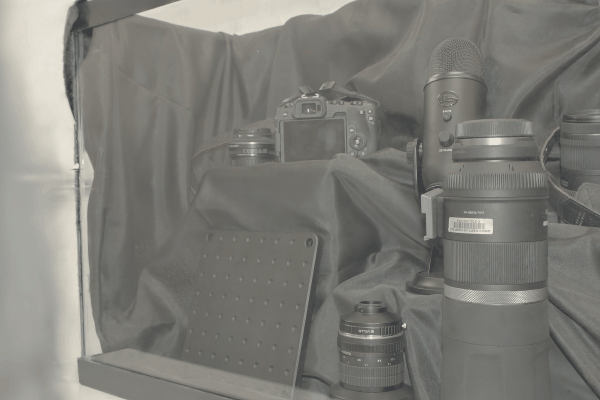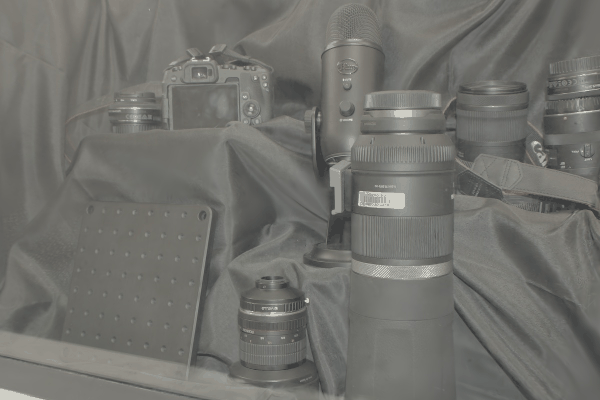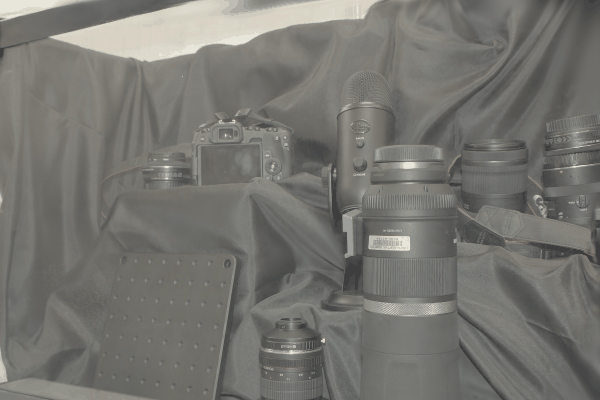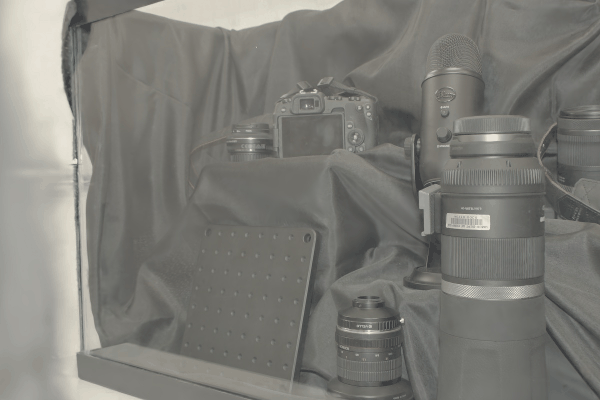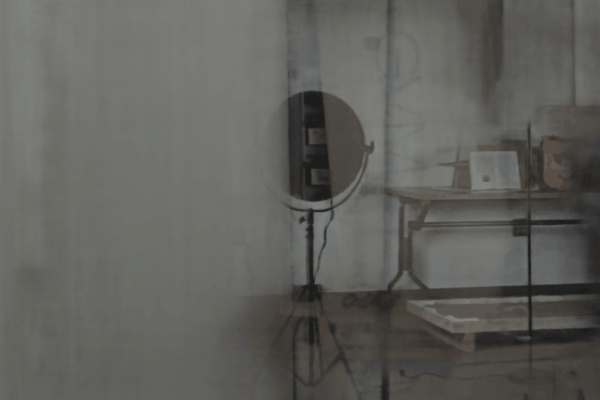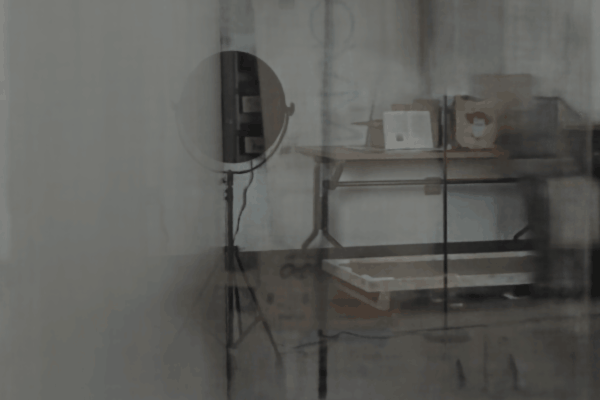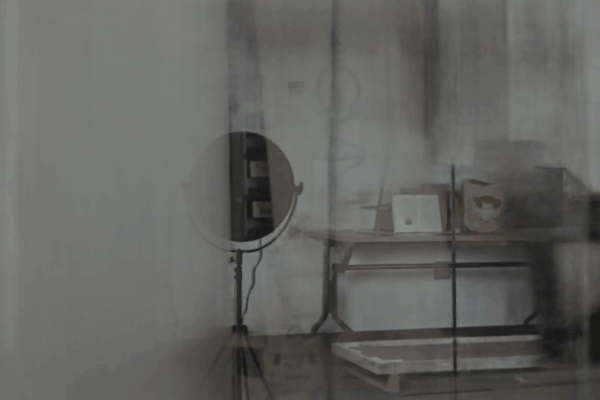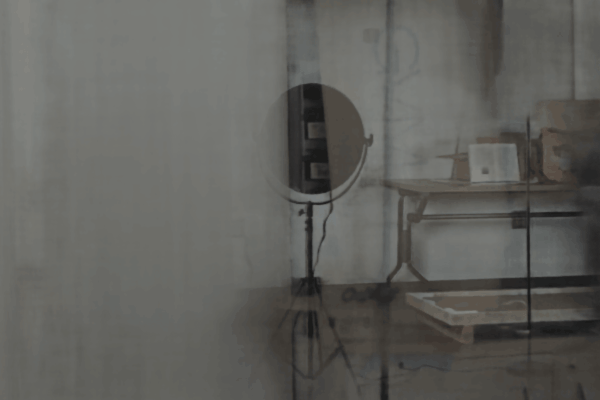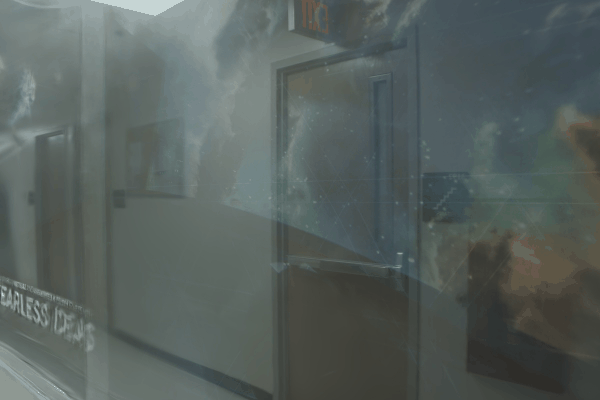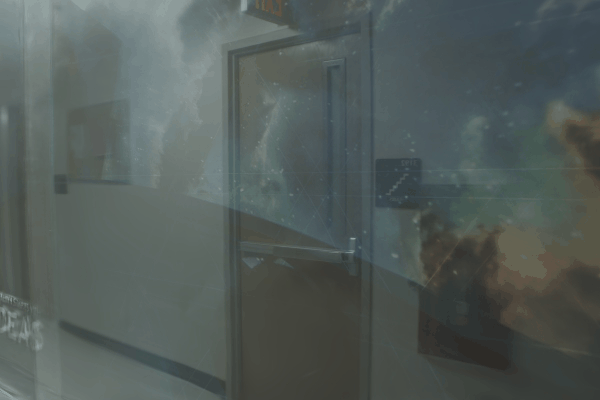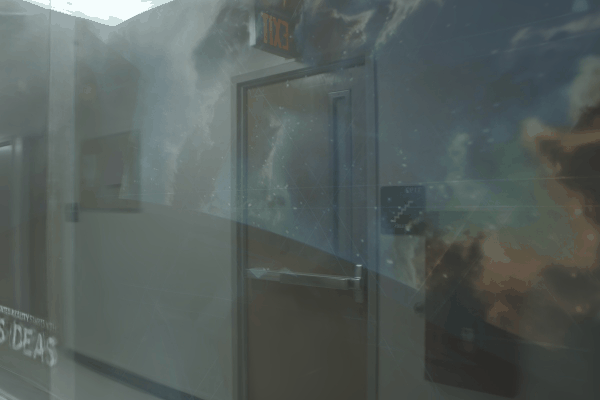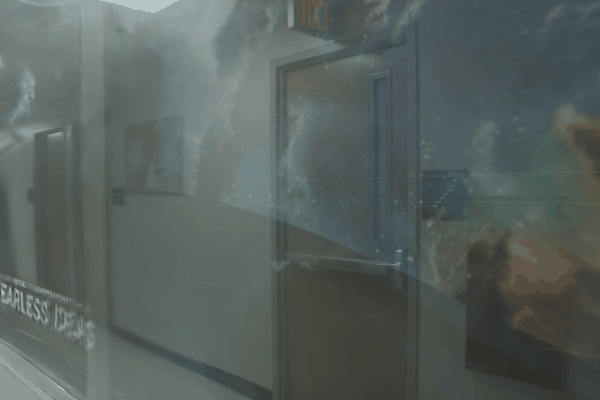



















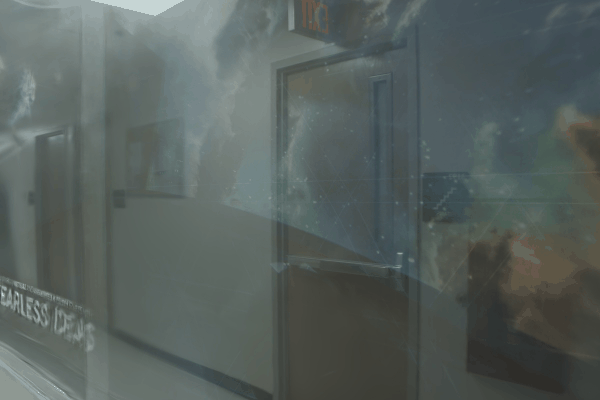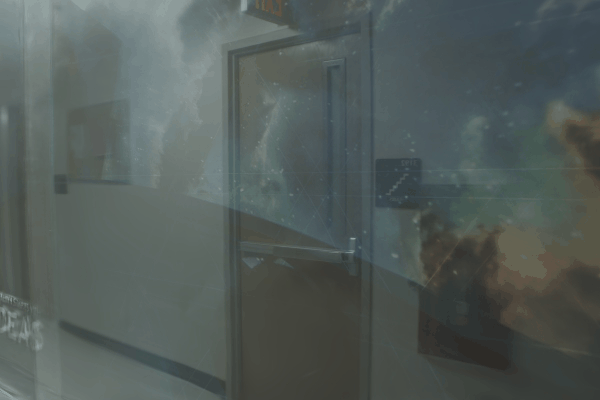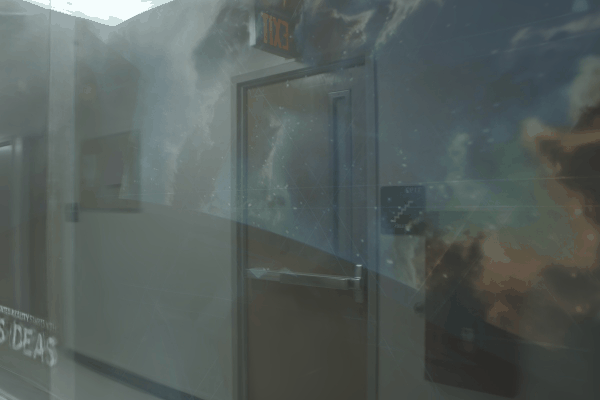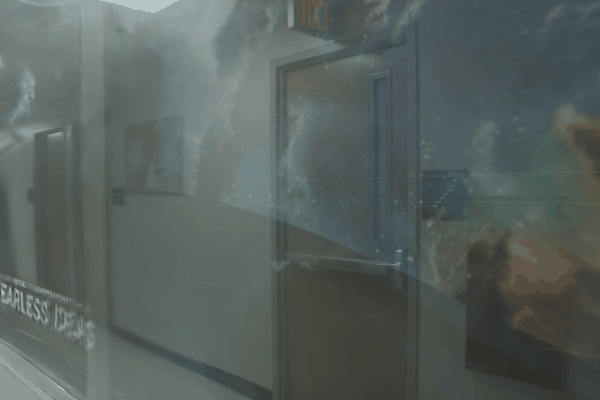














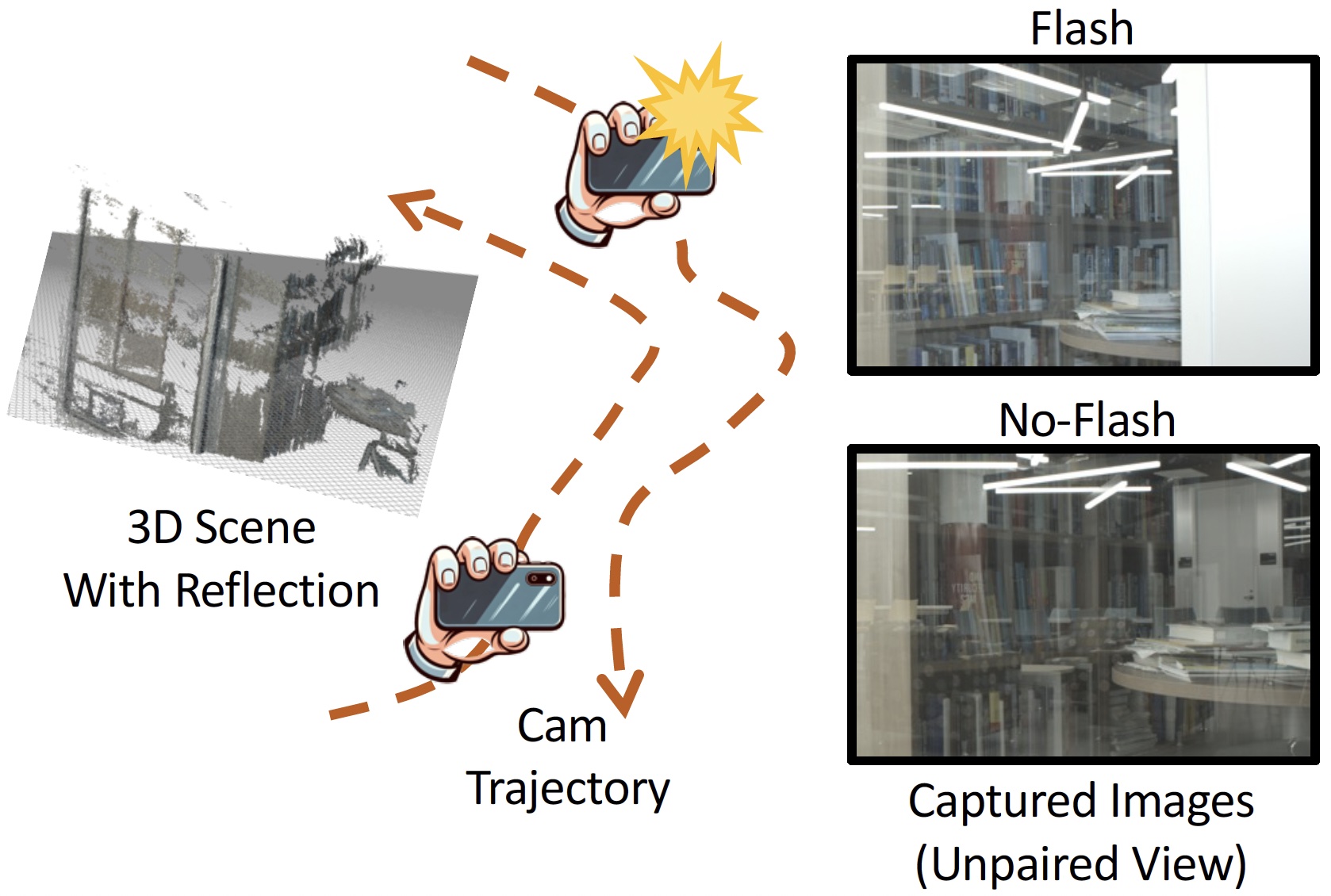
The user first captures a set of multi-view images with the camera flash on, and then captures another set of images with the flash off (no paired capture is requried). Our algorithm leverages these flash/no-flash images for 3D reflection separation.
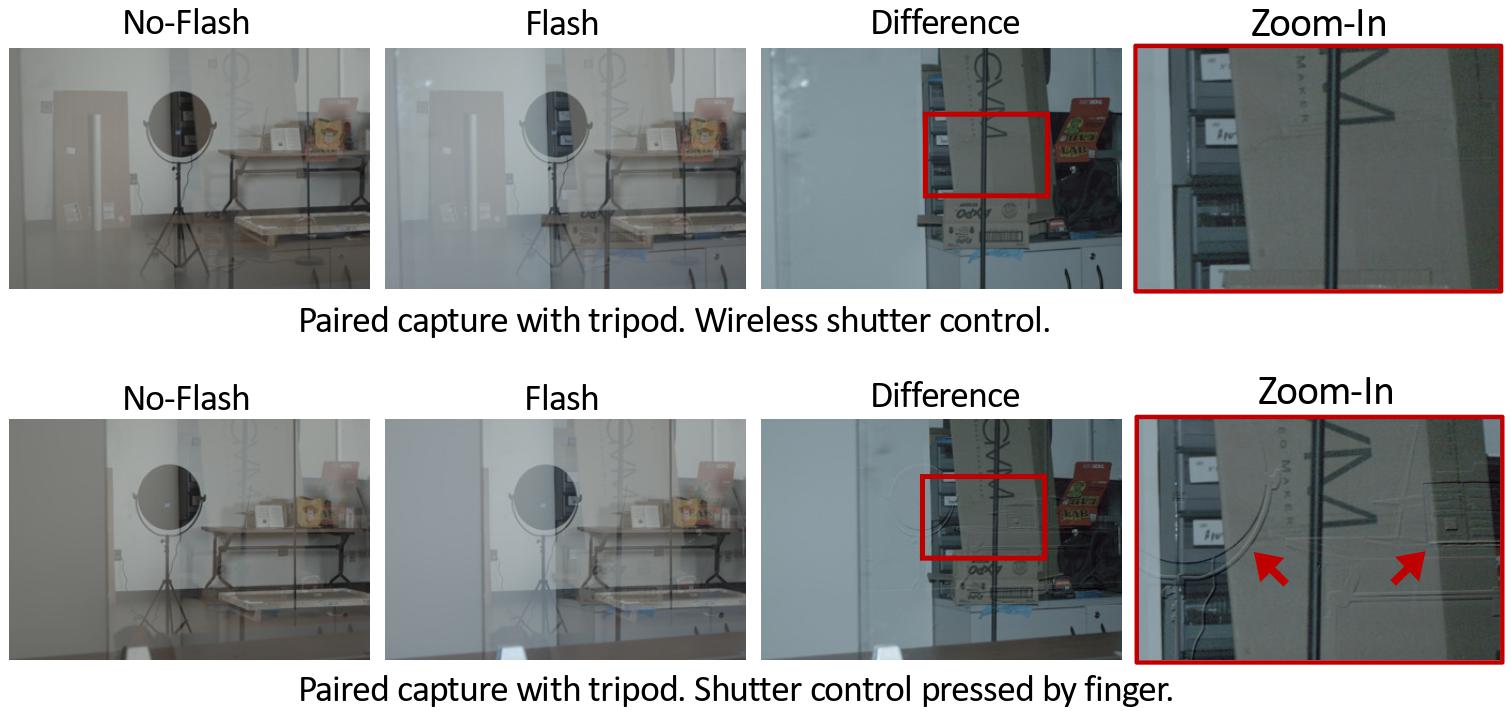
Flash/No-Flash For Reflection Removal. The difference between paired flash and no-flash images is equivalent to taking a photo with flash in a dark environment, which gives us a reflection-free image (top). This is because flash increases the transmission brightness, but not the reflection brightness. Notice pairs must be tightly aligned for this method to work. Even tiny vibrations such as pressing the shutter button even when using a tripod produce artifacts (bottom).
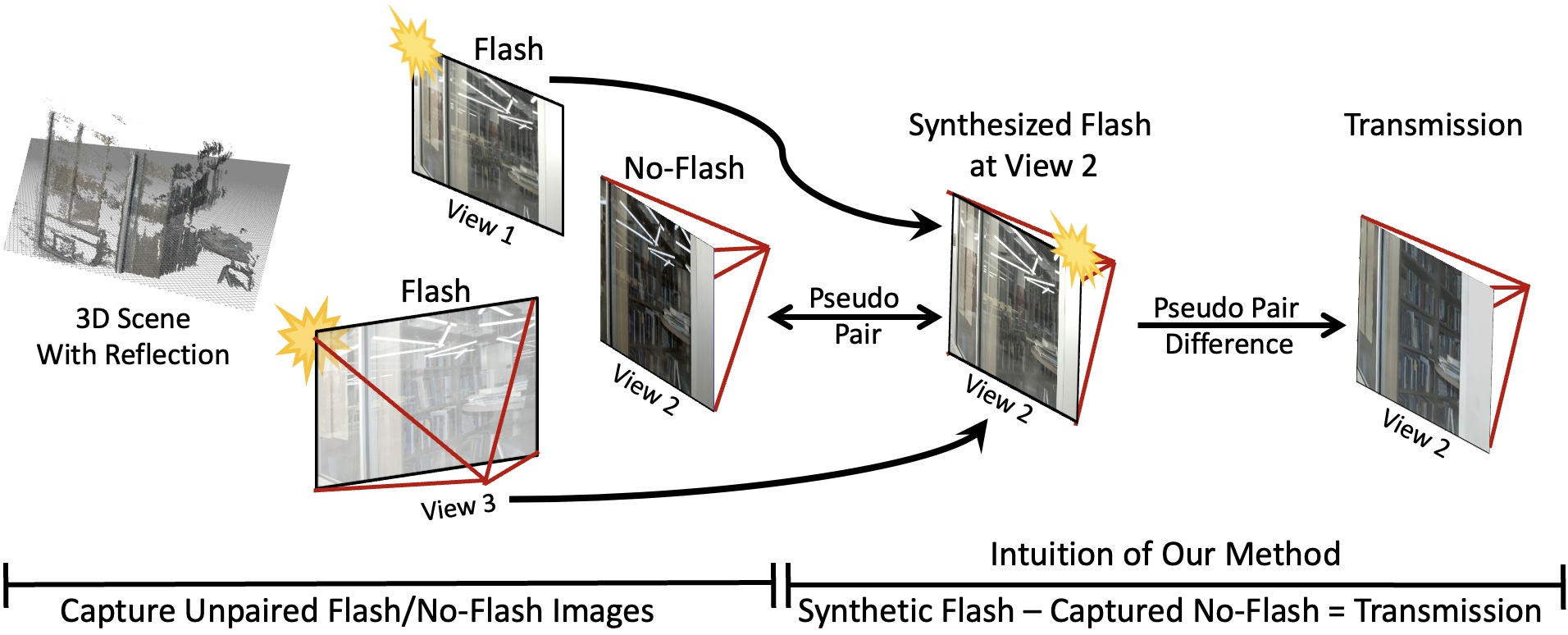
We create ``pseudo-pair'' of flash/no-flash images by novel view synthesis. During the data capture stage, we collect flash/no-flash images from different views (no paired capture is requried). For instance, if we have captured a no-flash image at View 2, we can learn a 3D representation of the captured flash images at other views, and then synthesize a novel view of the flash image at View 2. As such, we have created a pseudo-pair of flash and no-flash images at View 2. The key idea is that, by taking the difference between the pseudo-pair, we get the transmission component of View 2 that is free of reflection.
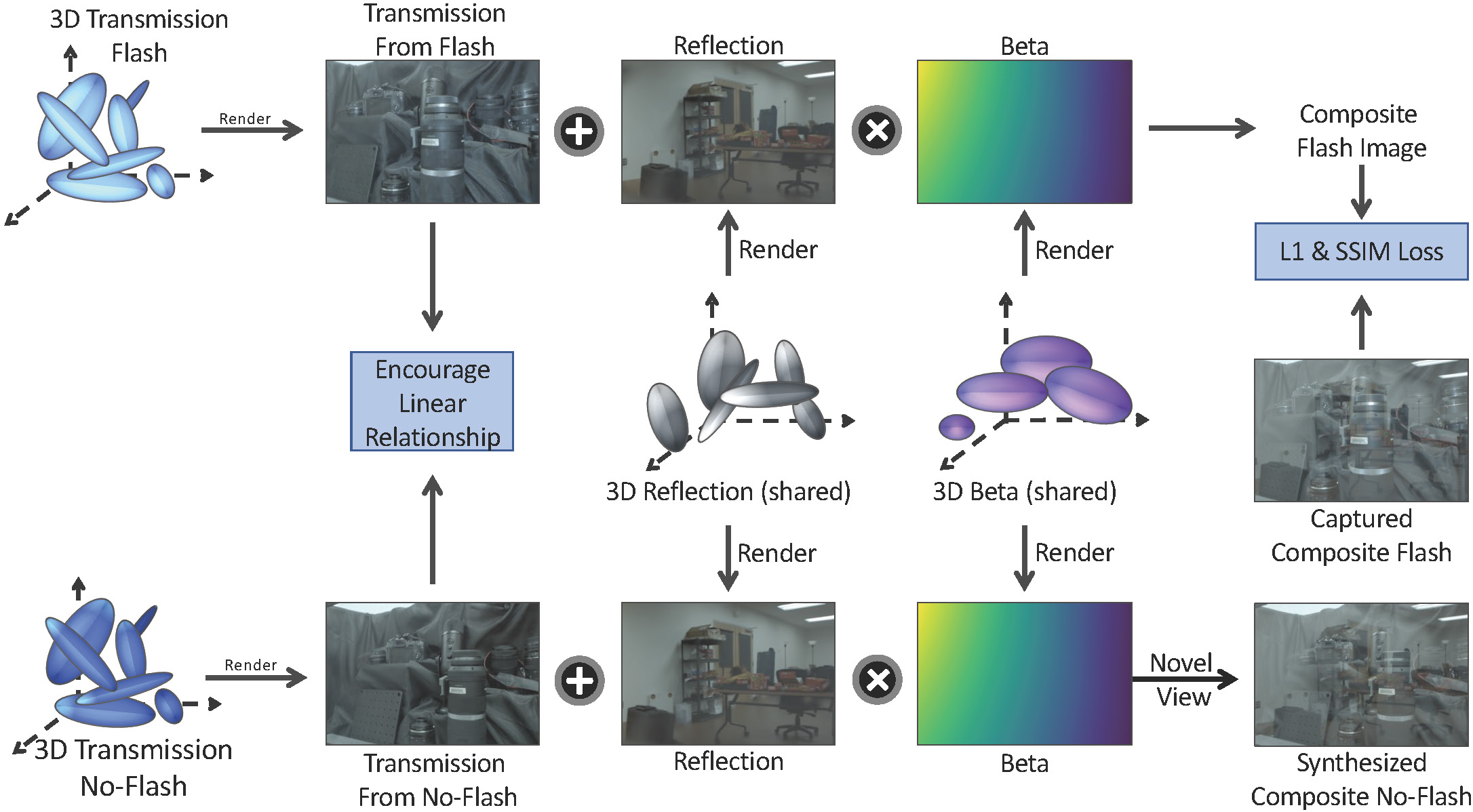
We jointly optimize 4 sets of 3D Gaussian Splats, including the transmitted scene taken with flash , the transmitted scene taken with no flash , the reflected scene , and the reflection ratio map Beta . Based on the Flash/No-flash idea, and are shared between the flash image and the no-flash image, and we encourage a linear relationship between and .